Preview: Those with disabilities have long adopted, adapted, and appropriated collaborative systems to serve as assistive devices. In a Minecraft virtual world for children with autism, community members use do-it-yourself (DIY) making activities to transform Minecraft into a variety of assistive technologies. Our results demonstrate how players and administrators “mod” the Minecraft system to support self-regulation and community engagement.
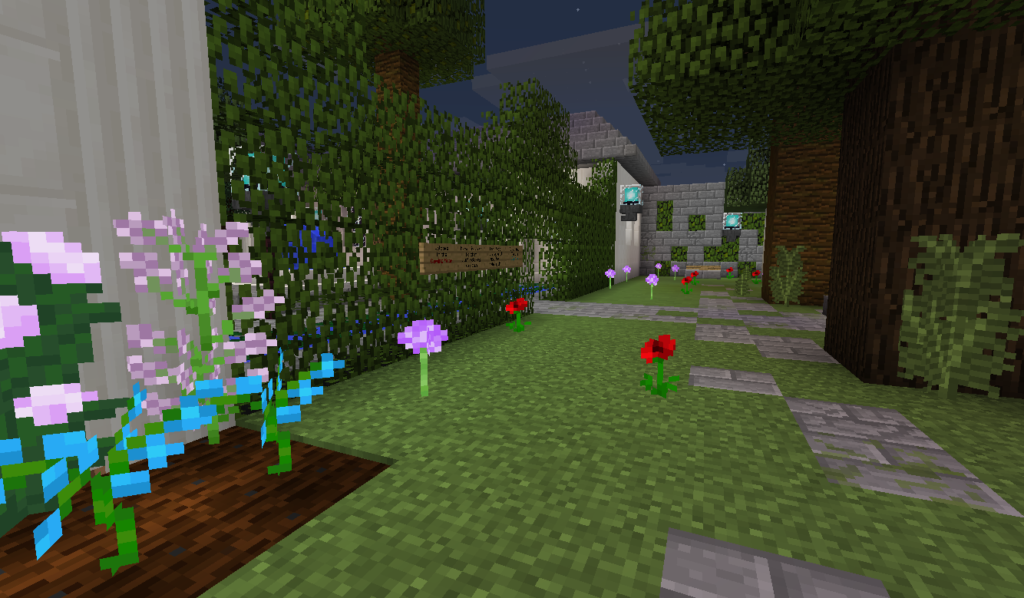
A calming, quiet garden in Minecraft.
“Need a place to calm down? Quiet? Peaceful? Choose a Calm Room to visit here. In these rooms [t]here is no chat. It’s a place to relax. Visit any time.”
If a child finds face-to-face conversations challenging and feels isolated from their peers at school, where can they go to make friends? How can people use currently existing systems to help those with disabilities, including children with autism? We studied how one online community, Autcraft, through a variety of social media platforms, augments and extends current platforms and transforms them into assistive technology for children with autism.
Autcraft is a Minecraft community for children with autism and their allies run by parent volunteers. The goal of the Autcraft community is to have a safe space for children with autism to play Minecraft free from harassment and bullying (for more information visit the Autcraft website). As part of our study, I have been conducting an on-going ethnography within the community (see our paper for details). This study included analysis of activity within the Minecraft server, forums, website, Twitter, Facebook group, YouTube, and Twitch.
Our analysis demonstrates how players and administrators “mod” the Minecraft system to support self-regulation and community engagement. This work highlights the ways in which we, as researchers concerned with accessible and equitable computing spaces, might reevaluate the scope of our inquiry, and how designers might encourage and support appropriation, enhancing users’ experience and long-term adoption.
Autcraft community members have modified Minecraft to do the following to help players internally regulate themselves and externally manage their engagement with others:
- Self-Regulation. Community members use Minecraft in a variety of ways to self-regulate, including both sensory regulation and mood regulation. Dealing with sensory overload can be a difficult experience for anyone with autism, particularly for children and adolescents who are still learning coping skills. Members of the Autcraft community have created spaces within the virtual world and the other platforms to help even the youngest members learn to deal with these sensory needs. Additionally, to help regulate mood, members are able to put into words their emotional experiences, safely share and vent their feelings with others, on the forums and through in-game chat. They can do this in Autcraft without the fear of reprisal from bullies or trolls—which is something they may fear in other online spaces. While this type of behavior may not be unique to Autcraft, the ability to vent in this safe space is possibly unique for the community members personally. They may have communication challenges in their physical environments that limit their abilities to express their feelings fully.
- Interacting with Others. Members of the Autcraft community have appropriated the entire ecosystem of technologies surrounding Autcraft to support interfacing and engaging with others. These efforts support engagement with both the internal community and across community boundaries by supporting sociality explicitly. One mod, teleportation, enables players to jump from one place to another in the Autcraft virtual world nearly instantly. This mod, which can be found on a variety of Minecraft servers, creates a “safer” virtual world experience and to support socialization among community members. Teleportation is available through various waypoints within the Autcraft Spawn area as well as through the text chat window. This teleportation functionality not only enables these quick avatar interactions, but also gives community members an ability that they do not have in the physical world. This helps support empowering these young community members to engage in socialization with their friends, when and where they choose.
Individual players appropriate the Autcraft virtual world to suit their own needs, shaping their virtual environment, embodied experience, and, in time, influencing the overall experience for everyone in Autcraft. As the children worked within the confines of the virtual world to make their environment more usable by appropriating with what was available, administrators are able to then iterate on these appropriated instances to re-appropriate the software itself. Thus, administrators, following the cues of the children within the virtual world, are able to instantiate these appropriations and make them available to everyone on Autcraft.
As a group, children with autism are doubly disempowered: both as children and as people living with disabilities. Here, however, we see how this kind of technological openness allows them to customize and create their own play spaces, a type of autonomy that is inherently empowering. This work explores how designers and researchers can learn by observing how even the youngest of users augment and appropriate mainstream technology to become assistive in their daily lives. This work highlights the ways in which researchers concerned with accessible and equitable computing spaces might reevaluate their scope of inquiry and how designers might encourage and support appropriation, enhancing the individualized experience and long-term adoption of assistive devices and systems. The appropriations we observed in Autcraft point to a future model where child-initiated modifications can guide research and design, providing greater access for disempowered communities.
For more details about our methods and findings, please see our full paper that has been accepted to ASSETS 2016 (to appear in October 2016). Full citation and link to the pdf below:
Kathryn E. Ringland, Christine T. Wolf, LouAnne E. Boyd, Mark Baldwin, and Gillian R. Hayes. 2016. Would You Be Mine: Appropriating Minecraft as an Assistive Technology for Youth with Autism. In ASSETS 2016. [PDF]
 Acknowledgements: We thank the members of Autcraft for the warm welcome into their community. We also thank members of LUCI and the anonymous reviewers for their feedback on this paper, and Robert and Barbara Kleist for their support. This work is covered by human subjects protocol #2014-1079 at the University of California, Irvine.
Acknowledgements: We thank the members of Autcraft for the warm welcome into their community. We also thank members of LUCI and the anonymous reviewers for their feedback on this paper, and Robert and Barbara Kleist for their support. This work is covered by human subjects protocol #2014-1079 at the University of California, Irvine.
Related Posts:

Preview: For members of the Autcraft community, they are not only coming to terms with their identity as autistic individuals, ...

I'm happy to announce that I will be the opening keynote at the Education in Games Summit this year in ...

Recently, I was interviewed for the Xceptional Leaders podcast series. In a follow up blog, I will relate some of ...





 Acknowledgements: We thank the members of Autcraft for the warm welcome into their community. We also thank members of LUCI and the anonymous reviewers for their feedback on this paper, and Robert and Barbara Kleist for their support. This work is covered by human subjects protocol #2014-1079 at the University of California, Irvine.
Acknowledgements: We thank the members of Autcraft for the warm welcome into their community. We also thank members of LUCI and the anonymous reviewers for their feedback on this paper, and Robert and Barbara Kleist for their support. This work is covered by human subjects protocol #2014-1079 at the University of California, Irvine.