This is a summary of the work presented at SCMS 2022. This is cross-posted on Medium: https://medium.com/p/d8ebbe436fa2
Play happens everywhere and is a universal human experience. However, questions of accessibility still challenge many playful spaces. As diverse as people are, there are a diverse set of needs in order to access an activity, interaction, or experience. We find, though, that disabled individuals are often not accommodated in playful places.
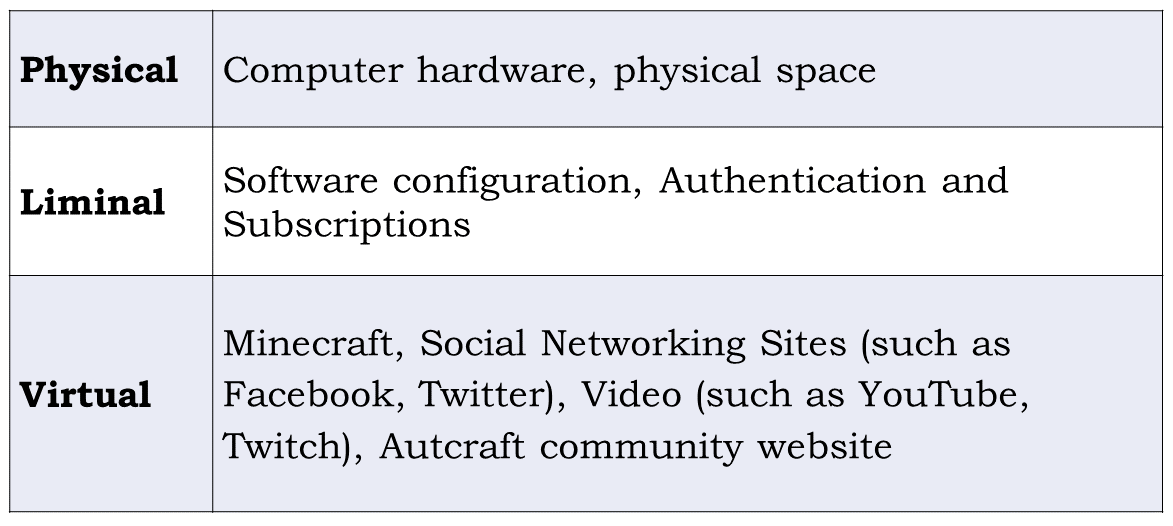
I turn particularly to online playful spaces where some disabled people may find the primary source of their interactions. These online spaces become community places, where people with like-interests congregate, form relationships, and have fun. For playful communities, creating access means both grappling with platform design, including appropriation and modification of technology, and iterating on community norms and expectations to accommodate community members.
In this presentation, using data from ethnographies from two different playful communities, I will explore how the platform and community values are entangled and impact not only the playfulness, but also the accessibility of the space [3,6].
Methods
For both the case studies used in this work, I used ethnographic methods where I was embedded as a participant observer in the community for an extended period of time. In each community, I collected data from my own observations, public social media content, and community produced content. This work is qualitative and while I use some mixed methods, such as surveys, I mostly use that to triangulate what I am already finding in my qualitative work. This means that this work goes very deep into some community spaces and narrows in on specific aspects of my work. In order to preserve the safety of the community members, everything is paraphrased, abstracted, or anonymized as appropriate.
I identify as disabled scholar and activist, which means I approach most of my research with a critical disability lens. I look at spaces through a lens of deconstructing ableism that is occurring there, as well as trying to better understand communities from the perspective of making members feel safe, included, and cared for.
Autcraft
The first ethnography was conducted in a community centered around the video game Minecraft — Autcraft — was founded to create a safe space for autistic youth [5]. The Autcraft community uses various methods including modifying game software, leveraging other social media platforms, and adhering to a strict code of conduct for members to address not only the needs of autistic youth, but to accommodate other access needs [3].
The Autcraft community uses a variety of technological platforms in their community, but it is centered around the video game Minecraft. They use plug-ins and modifications to the software in order to make the game more accessible for the players. There are many different ways the community creates “access” through technological means and many of these technological implementations have been iterated on over time.
The majority of communication in the game world happens via text or through avatar interactions, which are quite simplified compared to some other multiplayer games. This was another intentional choice by the community. If the text in the image above were happening live, it could be moving up the screen fairly quickly. While this is still preferred to other modes of communication, it has its challenges and takes some getting used to.
After learning of a player in the community who was losing their vision, they added a new plug-in to the game in order to make the text chat more accessible. Now the different lines are separated by a symbol of the players choice, such as the dash. Specific titles and the player’s name is also highlighted in different colors. In making this change, the community ended up making text chat more accessible for many of the players.
The reason many people join the Autcraft community is because they had difficulty fitting in, finding friends, or, more broadly speaking, getting access to the play in a Minecraft space. Therefore, for many on Autcraft, being helpful and supportive is one of the most important parts of their sociality. The community has found it important enough to write into their rules and actively encourages this behavior through rewards, such as special titles such as member of the week.
Community describe hanging out with their friends on the Autcraft community much in the same way other youth online have. They spend time with their Autcraft friends online by interacting through forums, instant messaging, and “hanging out” in the Autcraft virtual world. And although not typically physically collocated, these youth on Autcraft consider these relationships to be meaningful friendships.
BTS’s ARMY
The second, ongoing ethnography is being conducted within the ARMY community, the fandom for the Korean musicians, BTS [4]. Much like the Autcraft community, the ARMY community is global. Unlike the Autcraft community, ARMY is a community made of loose-ties and more porous boundaries for community membership [2]. Therefore, how the community engages in play and accommodates access needs of members is notably different from the Autcraft community, as there are no central individuals making decisions about accommodations.
Additionally, because ARMY tends to use public social media platforms, the amount of control they have over the technology is very different from Autcraft. One way the community creates access is by smaller sub-communities using whatever platforms work for them. Smaller groups of ARMY, then, might be found on a modified Discord server or in a group chat. BTS, and the band’s use of various social media platforms, might also dictate what platforms are the most popular among ARMY.
More often, the social infrastructure is altered and iterated upon in order to create access. Specialized accounts to create spaces for disabled or Deaf — or any other subgroup — exist to help foster support and push for more access. For example, as a disabled ARMY, I have been pushing for more alt text to be incorporated in community members’ posts on social media. This also means asking the social media platforms to create more access for users as well.
This sort of activity is important because much of ARMY’s play are fan edits, parody accounts, threads of music and videos, art, and commentary about BTS. In fact, ARMY and BTS often play together, each creating content, communicating via various social media platforms, and share the same goals. The play is very referential, often including layers of inside jokes. For example, there is a plethora of content that explicitly references BTS’s known love for chicken [1].
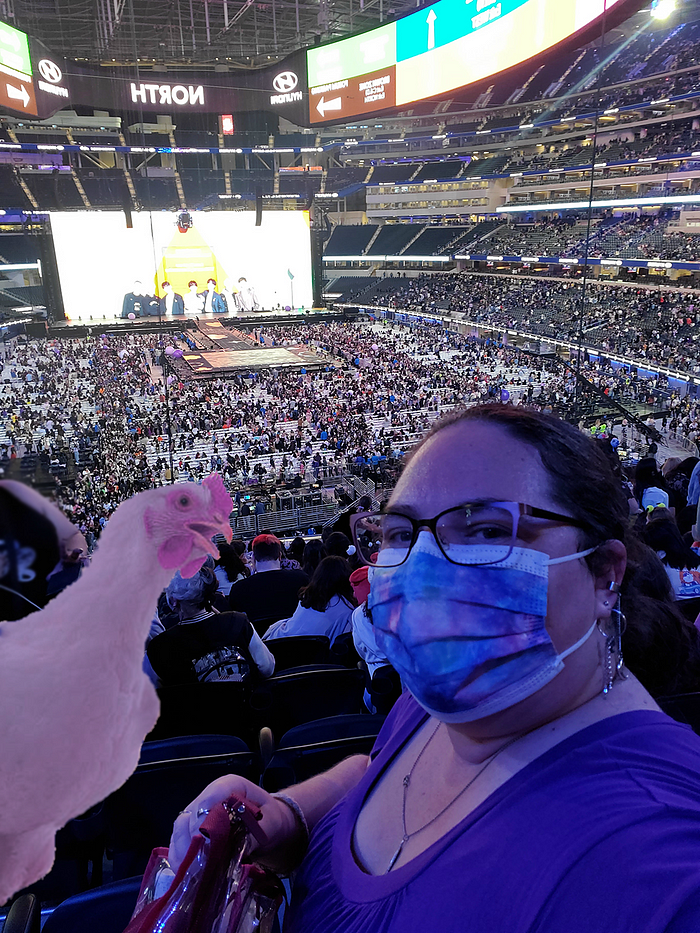

Like the Autcraft community, ARMY are mindful of social justice issues, especially with regard to access. In both communities, we see how play is both a playful activity, but also an important mechanism for more serious endeavors. This might look like an Autcraft member creating a series of YouTube videos of their game play as an anti-bullying campaign. Or this might be a member of ARMY creating a thread of edited BTS content to highlight the international sign the band used in their Permission to Dance video.

Both communities are also doing the work of correcting misconceptions and pushing back against stigma about themselves. These misconceptions occur because outsiders do not understand the community (often harboring sexism, misogyny, racism, and ableism towards both communities). Particularly, because these are communities of play, they are also often dismissed as ultimately inconsequential by outsiders. This is something both communities would vehemently protest, and do.
Creating Access to Play
Together, these studies show how communities leverage their playful qualities to appropriate and modify the technological and social make-up of the group in order to accommodate a diverse set of community members. From this, we are mostly left with more questions about “play” and “access.” Where is play taking place and can we support ideas of play for the sake of play at the same time play is also being used for more serious business? How is access being created in these various social spaces and what can communities do when they are at the mercy of the technology available to them?
In both communities, we see play being the platform for serious, even life-impacting, interests of community members (e.g., anti-bullying campaigns, grappling with both community-wide and individual trauma). With the advent of the COVID-19 pandemic, these communities became that much more important for its members, as they became the only means of socializing and forming relationships with people outside their homes and places of work. These playful communities were not just a place of leisure or a creative outlet. They are also a place to form meaningful connections with other people.
At the same time, these playful communities are addressing various questions of access. In this talk, I started to illuminate some of the ways communities accommodate disabled community members. The work these communities are doing should be noted because how communities play and what that play is doing for members of communities can be a starting point for understanding these otherwise marginalized groups.
And you can watch a pre-recorded version of the presentation here:
References
1. @bock_twt. 2020. Bantam Seoyeondon: BTS ARMY Shenanigans. In 2020 Rhizome Connect Virtual Conference and Convention. Retrieved September 5, 2021 from https://rhizomeconnect.com/2020/expo-hall/shenanigans/
2. So Yeon Park, Nicole Santero, Blair Kaneshiro, and Jin Ha Lee. 2021. Armed in ARMY: A Case Study of How BTS Fans Successfully Collaborated to #MatchAMillion for Black Lives Matter. CHI 2021: 14.
3. Kathryn E. Ringland. 2019. A Place to Play: The (Dis)Abled Embodied Experience for Autistic Children in Online Spaces. In Proceedings of the 2019 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1145/3290605.3300518
4. Kathryn E. Ringland, Arpita Bhattacharya, Kevin Weatherwax, Tessa Eagle, and Christine T. Wolf. 2022. ARMY’s Magic Shop: Understanding the Collaborative Construction of Playful Places in Online Communities. In Proceedings of the 2022 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems.
5. Kathryn E. Ringland, Christine T. Wolf, Heather Faucett, Lynn Dombrowski, and Gillian R. Hayes. 2016. “Will I always be not social?”: Re-Conceptualizing Sociality in the Context of a Minecraft Community for Autism. In CHI 2016.
6. Tanya Titchkosky. 2011. The Question of Access: Disability, Space, Meaning. University of Toronto Press, Toronto, Ontario, Canada.