As I mentioned in Part 1 last week, I will be going over my various methods for managing my workflow. Today, I will be discussing general task management.
Task Management
First, I will start discussing my workflow with the tricky topic of task management. I’m starting here because my task management system is fairly easy in comparison to some of my other workflow mechanisms.
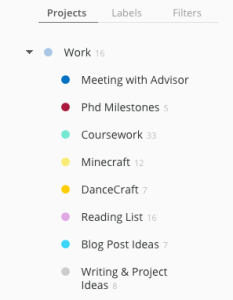
My tasks can be broken down into Work and Personal. I will discuss my Work tasks here even though I generally use the same exact system for Personal tasks as well (because it’s all about keeping myself sane). Work tasks are then broken down into their various categories: general, PhD milestones, reading, writing, research (which is broken down by project). You can see these listed as “Projects” in Todoist below.
For task management I use Todoist. I have tried several different to do list apps over the last few years and Todoist works the best given my needs. It meshes well with my other tools, is robust, and very flexible. It also has the added benefit of being somewhat reinforcing with its fun “karma points.”
Todoist is great because it lets you write out your task such as “write 1500 words every weekday” and it will figure out when the next time you need to complete the task is. You can read about other cool ways to use Todoist here and here.
Tasks for me, once divided into their subcategories, fit into a few different molds: one-off tasks, repeating tasks, and floating tasks.
First are the one-off tasks. These are things I only have to do once and then they are done. These are easy to just go to Todoist and say “write final paper for Inf 232 March 14.”
Second are the repeating tasks. These include my daily reading and writing (self-imposed) requirements, among other things. For example, “1500 words very weekday.” This would also include my meetings and classes. For example, “lab meeting every Monday until June 9” or “send weekly update every Monday noon.” And yes, I include everything as a to do item on my list – tasks, drafts, things I have read, meetings, and so on.
These first two task types (the one-off and the repeating) then appear on my daily or 7 day task list. I can see them coming or I see them as past due if I missed something. I use this extensively in my daily routine. This is how everything gets done and I stay on track. I even include tasks such as “update blog every Thursday” and “clean out email inbox every Friday” just to keep up with the things I normally put off as unimportant (and, therefore, never get done).
Third are the tasks that do not strictly have a due date. These floating tasks are more likely to be things such as my reading list or writing ideas. My reading list is just a list of things I plan on reading (soon). I add to it as new articles come across my Google filters or my advisor suggests an article. Writing ideas are just brief thoughts about things I might want to write about at some point. They are good for the days I have writers block and I can’t think of what to write. I include all kinds of things in this list including blog ideas, thoughts about my research, potential future articles to flesh out for a conference or journal, even things that might evolve later into new research or my dissertation. I also keep a floating task list of things I need to discuss with my advisor. That way, I can just pull up my “Meeting with my Advisor” list and check things off as I go over them with her.
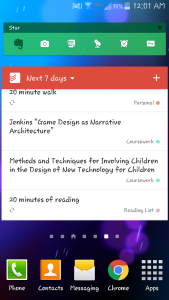
I keep my 7 day task list at hand on my phone, so I can check things off on the go:
That sums up my basic task management. Next week, in Part 3, I will discuss how I manage my readings and citations.